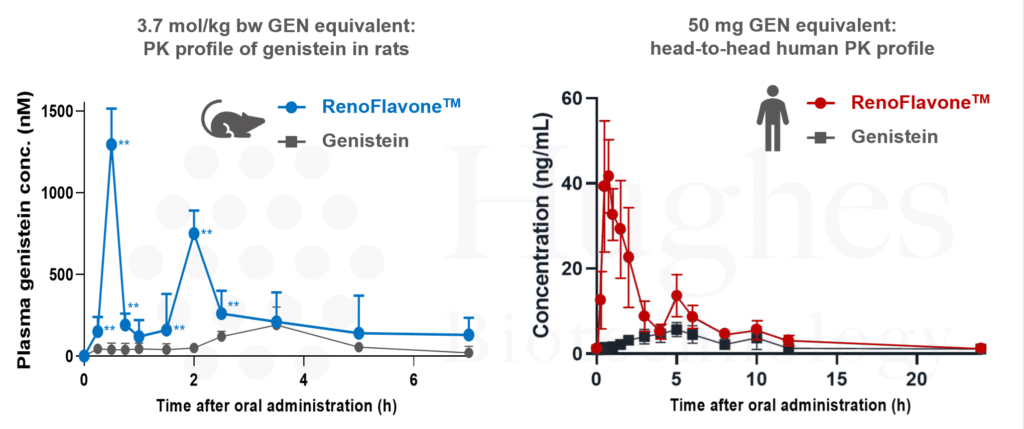
50 mg GEN equivalent: head-to-head human PK profile
Patents across United States, Euporean Union, Korea, Japan and Taiwan, with applications focusing on postmenopausal bone health.
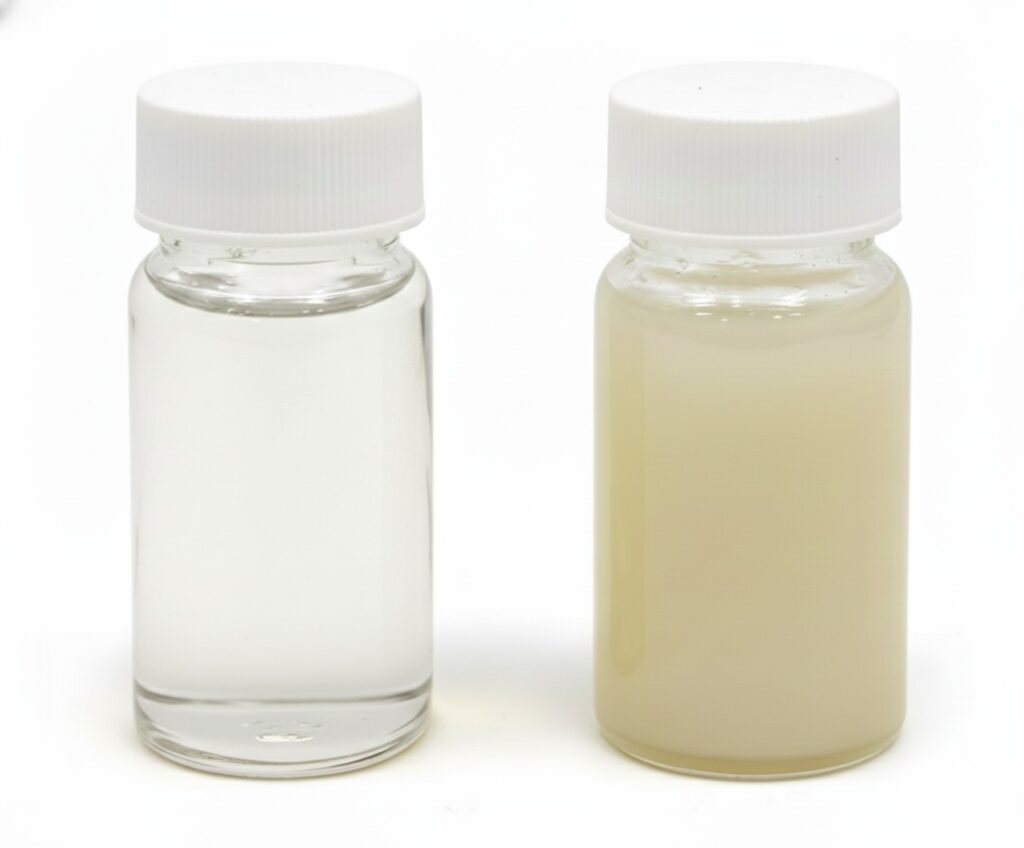

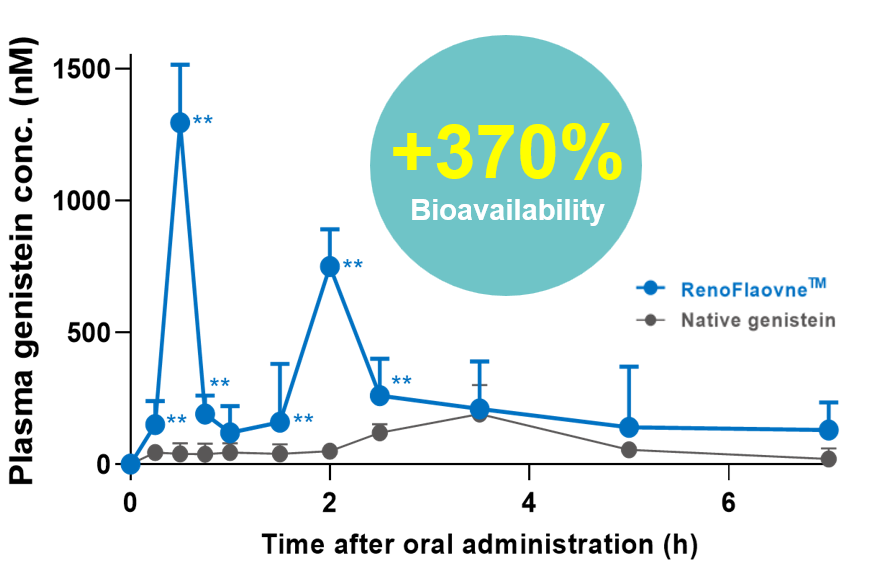
Dose: 80mg/20mL
(Left) RenoFlavone™ solution
(Right) Native genistein suspension
Journal of functional foods 13 (2015) 323–335
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.01.008
This study confirmed the oral toxicity and genotoxicity profile of standardized RenoFlavone™ under good laboratory practice (GLP) conditions.

Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human trial
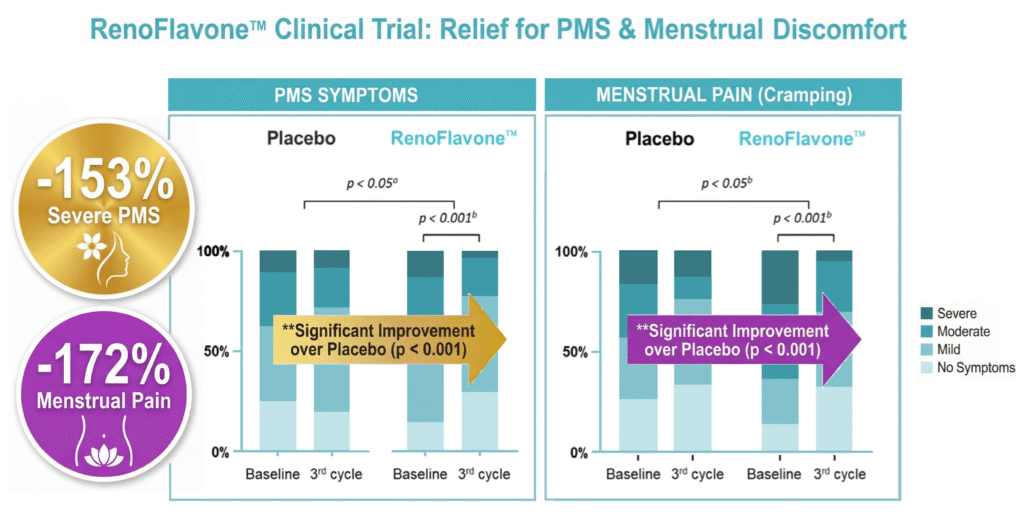
A sample of 120 women (aged 18-40) suffering from primary dysmenorrhea were randomly assigned to either a placebo group or a RenoFlavone™ group, and a 3-month human trial was conducted. Effects of RenoFlavone™ intervention on the PMS and dysmenorrhea feeling. Comparison of baseline vs 3rd cycle values in each group (Wilcoxon test)a and between groups (Mann-Whitney U test)b.The results showed a statistically significant improvement in PMS-related symptoms with RenoFlavone™.
Questionnaire Assessment :
● PSST (Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool)
● MDQ (Menstrual Distress Questionnaire)
● SF-MPQ (Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire)
● VAS (Visual Analogue Scale for Pain)
Reference:
Cannabinoid receptor 1 antagonist genistein attenuates marijuana-induced vascular inflammation
Cell, Volume 185, Issue 10, 1676 – 1693.e23
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(22)00443-3

Journal of Functional Foods 58 (2019) 171–179
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.04.063
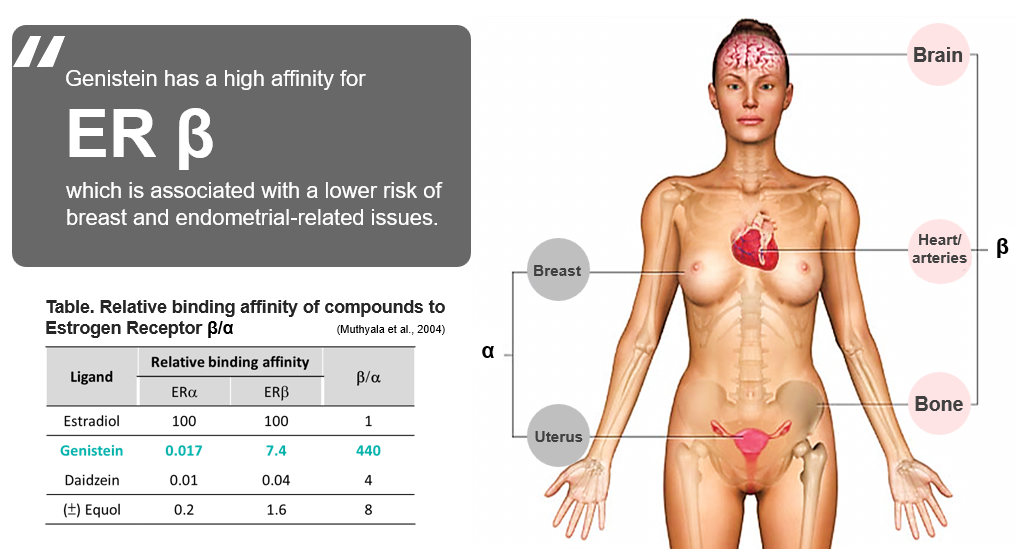
Genistein acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator, showing a stronger affinity and more stable binding for the Estrogen Receptor beta (ERβ) than the alpha receptor (ERα).
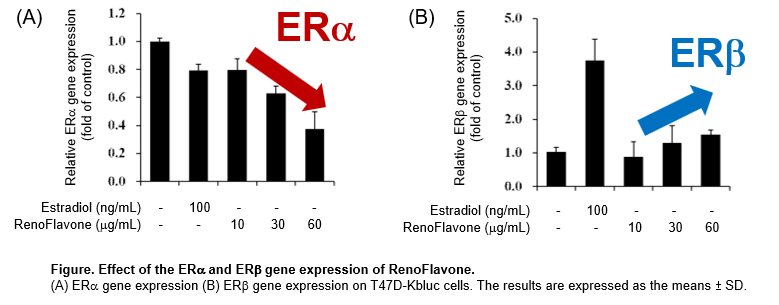
Upon administration of RenoFlavone™, the mRNA expression of ERα decreased in a dose-dependent manner and the mRNA expression of ERβ increased.
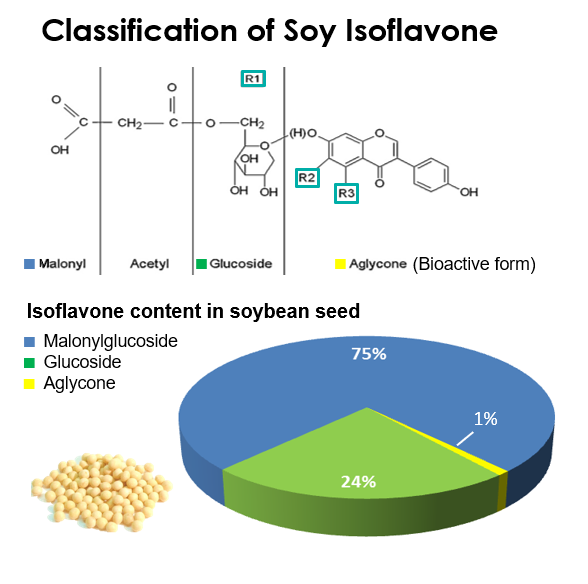
Isoflavones are a type of phytoestrogen commonly found in soybeans and soy-derived foods. There are 12 isoflavone isomers and genistein is one of them, which is also recognized as the most bioactive. Several biological effects of genistein have been reported in preclinical studies, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiviral activities, as well as effects on angiogenesis, estrogen, and pharmacological activities related to diabetes and lipid metabolism.